Solar and Planetary Systems
The team conducts research on three themes:
(1) Solid planets and satellites of the solar system
(2) Asteroids and comets
(3) Exoplanets
Using instruments aboard space missions, the team measures the composition of planetary surfaces and atmospheres.
The aim is to characterize the processes of physicochemical and climatic evolution in order to trace the history of the planets.
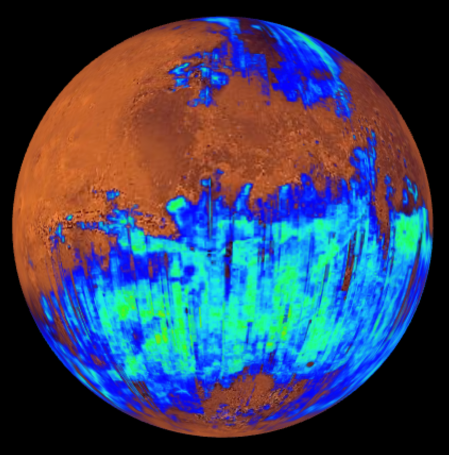
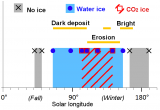
Particular attention is paid to water and carbon: where and in what state are they found in the Solar System today? What is their history, from primordial inputs to contemporary processes? What is Earth's place in the diversity of planets and exoplanets?
The team's recent research has focused in particular on Mars, water- and carbon-rich asteroids, the icy moons of Jupiter, Mercury and the atmospheres of exoplanets. The composition of these objects is studied using spectrometers and visible and infrared imagers.
Our approach combines observation, data analysis, numerical modeling and laboratory simulation. One of the team's distinguishing features is its direct involvement in the construction of numerous space instruments, with a constant concern to combine scientific and technological challenges. The team also works on microscopic analysis analysis of extraterrestrial samples, in close collaboration with the astrochemistry team.