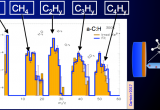
A multidisciplinary team involving researchers from IAS, IPNO, ISMO, and CSNSM in Orsay, and GSI in Darmstadt (Germany) has characterized in the laboratory the effects of heavy cosmic rays on the structural change and sputtering of small carbonaceous species released when cosmic rays, simulated and accelerated at the GSI accelerator, hit a carbonaceous interstellar dust grain analogue. The measurements performed during such simulations allow knowing the processes induced by radiations observed in space and their relative importance. The objective of these studies is to provide data on the evolution of the interstellar material, to understand its further evolution and provide constraints for modelers of astrophysical environments.
You are here
Nabila Aghanim, CNRS Directeur de Recherche at the Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale in Orsay has just received the CNRS Silver Medal, a distinction, which « honours every year researchers for the originality, the quality, and the significance of their work, recognised both in France and internationally, contributing thus to the influence of the CNRS and to the excellence of French research »
The Sun is currently in a quiet phase ; the next activity peak is is expected to happen in about five years, but in any event, a big solar-storm can strike anytime, not just at the peak of the solar cycle. Scientists and representatives of industrial sectors affected by space weather met at the Met Office to discuss how the solar-flare forecasting system FLARECAST should be designed to best serve user needs.
Led by Nabila Aghanim, the ByoPiC project (funded by an ERC Advanced Grant) aims at solving a key issue in astrophysics and cosmology: Where are the baryons hidden today in the cosmic web?
IAS is participating to the national open lab day "Fête de la Science" in the week of October 10th. After visits by students from several schools, the laboratory will be open for the general public on Sunday October 16th, from 2 to 6PM.