ROSEBUD is an experiment for the direct detection of Dark Matter, set up in the Canfranc tunnel (Pyrénées)
Contact at IAS: Noel Coron

ROSEBUD is an experiment for the direct detection of Dark Matter, set up in the Canfranc tunnel (Pyrénées)
Contact at IAS: Noel Coron

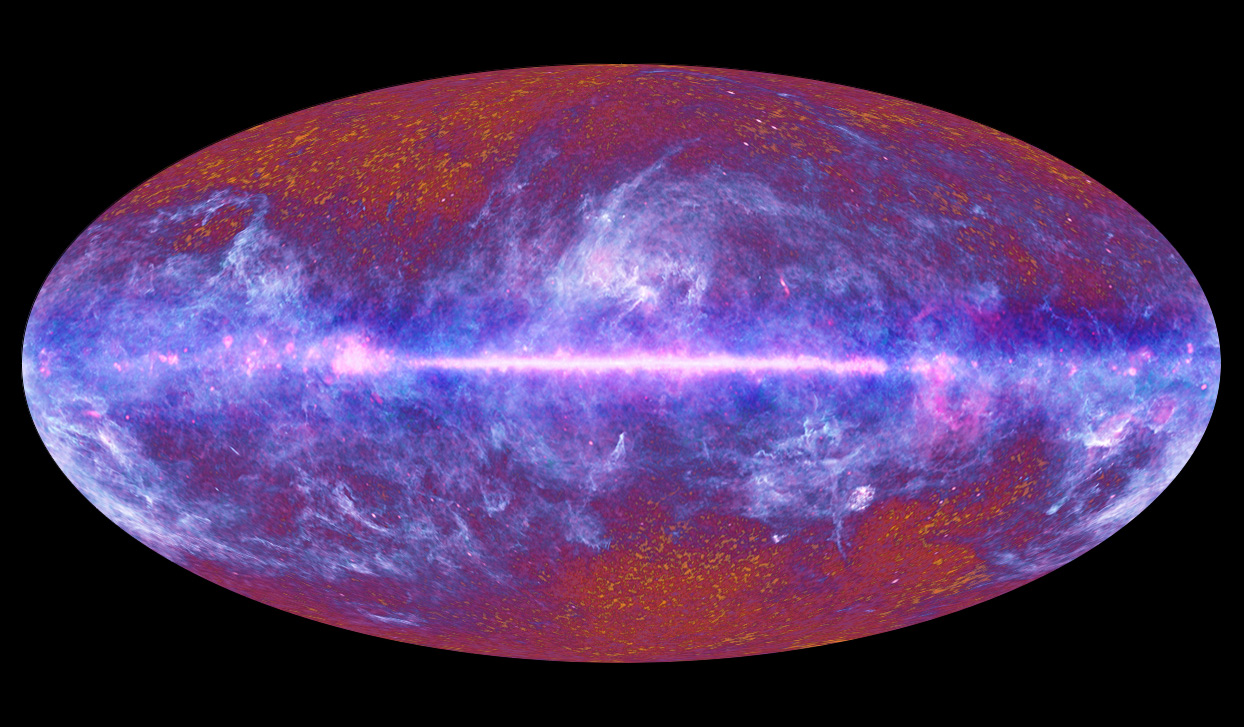
Planck enables us to answer some of the most important questions of modern science: How did the Universe begin, how did it evolve into its current state, and how will it evolve in the future? The objective of Planck was to analyse, with unprecedented precision, the remnants of the radiation that filled the Universe right after the Big Bang, and that we observe today as the Cosmic Microwave Background.
Contact at IAS: Nabila Aghanim & Jean-Loup Puget
PILOT (Polarized Instrument for Long wavelength Observation of the Tenuous interstellar medium) is a balloon-borne astrophysics experiment (CNES) designed for the measurement of the polarised light emmitted by interstellar dust grains.
Contact at IAS: Bruno Maffei
Euclid is an ESA mission that will map the geometry of the Dark Universe. The mission will investigate the distance-redshift relationship and the evolution of cosmic structures by measuring shapes and redshifts of galaxies and clusters of galaxies out to redshifts ~2, or equivalently to a look-back time of 10 billion years. In this way, Euclid will cover the entire period over which Dark Energy played a significant role in accelerating the expansion of the Universe.
Contact IAS: Nabila Aghanim & Hervé Dole
The European Space Agency's Herschel Space Observatory (formerly called Far Infrared and Sub-millimetre Telescope or FIRST) has the largest single mirror ever built for a space telescope. At 3.5-metres in diameter the mirror will collect long-wavelength radiation from some of the coldest and most distant objects in the Universe. In addition, Herschel is the only space observatory to cover a spectral range from the far infrared to sub-millimetre.
Contact at IAS: Alain Abergel & Alexandre Beelen

L'observatoire spatial Herschel de l'Agence spatiale européenne (anciennement appelé FIRST pour Télescope Infrarouge Lointain et Submillimétrique en anglais) a le plus grand miroir d'un seul tenant jamais construit pour un télescope spatial. À 3,5 mètres de diamètre, le miroir collecte le rayonnement de grande longueur d'onde de certains des objets les plus froids et les plus lointains de l'Univers. En outre, Herschel est le seul observatoire spatial à couvrir une gamme spectrale allant de l'infrarouge lointain au sub-millimétrique.
Contact à l'IAS: Alain Abergel & Alexandre Beelen

Euclid est une mission de l'ESA conçue pour cartographier la géométrie de l'Univers sombre. La mission étudiera la relation entre distance et décalage spectral vers le rouge (redshift), ainsi que l'évolution des structures cosmiques par la mesure des formes et des redshifts z des galaxies et des amas de galaxies jusqu'à z ~ 2 (ou de manière équivalente à un temps de retour en arrière de 10 milliards d'années). De cette façon, les observations d'Euclid couvriront l'ensemble de la période pendant laquelle l'énergie sombre a joué un rôle important dans l'accélération de l'expansion de l'Univers.
Contact à l'IAS: Nabila Aghanim & Hervé Dole

ROSEBUD est une expérience de détection directe de la matière noire installée dans le tunnel du Canfranc (Pyrénées)
Contact à l'IAS: Noel Coron
Definition: Rare Object SEarch with Bolometers UndergrounD
Objectif scientifique:
Détection directe de la matière noire du halo galactique

Planck permet de fournir des réponses à certaines des questions les plus importantes de la science moderne: comment l'Univers a t-il commencé, comment a t-il évolué vers l'état que nous observons aujourd'hui, et comment peut-il continuer à évoluer dans le futur? L'objectif de Planck a été d'analyser, avec la plus haute précision jamais atteinte, les restes du rayonnement qui remplissait l'Univers juste après le Big Bang, ce que nous observons aujourd'hui comme le Fond Diffus Cosmologique.
Contact à l'IAS: Nabila Aghanim & Jean-Loup Puget
