Astrophysicists consider that around 40% of the ordinary matter that makes up stars, planets and galaxies remains undetected, concealed in the form of a hot gas in the complex cosmic web. Today, IAS scientists may have detected, for the first time, this hidden matter through an innovative statistical analysis of 20-year-old data.
You are here
Archive
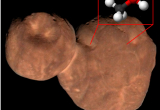
On October 21st, 2020, the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft succeeded in touching asteroid Bennu to collect samples from the surface. Launched in September 2016 and in orbit since December 2018, it was doing a detailed survey of the surface to map and select the best sample collection site. OSIRIS-REx will deliver the samples to Earth in September 2023.
How to measure and visualize in 3D the composition and structure of a micrometric extraterrestrial grain without destroying it? Researchers from the "Astrochemistry and Origin" team of the IAS and from the SOLEIL synchrotron, in collaboration with two Japanese laboratories, have shown that this is possible. Coupling IR and X-ray micro-tomography the scientist analyzed samples from the asteroid Itokawa, collected by the Hayabusa probe (JAXA).
Frozen surfaces of small bodies in the outer Solar System are exposed to cosmic and solar energetic ions. Thanks to laboratory experiments, scientists from the “Astrochemistry and Origins” team at IAS and the Florida Space Institute (USA) estimated the alterations induced by ion irradiation on the methanol-rich surfaces of such objects.
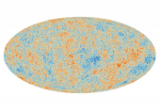
The Planck collaboration has just published its last series of articles, for a total of 164. These papers have been cited more than 90,000 times, which demonstrates the long lasting influence of this experiment for cosmology, including the study of the mass of neutrinos, the density of dark matter, the characteristics of primordial fluctuations, the formation and evolution of galaxies and clusters or even the magnetic field of the Milky Way.
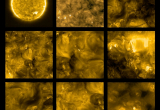
The first images from ESA’s new Sun-observing spacecraft Solar Orbiter have just been released. Solar Orbiter, launched on 10 February, completed its commissioning phase in mid-June and performed its first close approach to the Sun. Shortly thereafter, the European and US science teams behind the mission’s 10 instruments were able to test the entire instrument suite in concert for the first time.
Despite the drastic constraints driven by the sanitary limitations to technical activities at IAS, and the travel ban to Japan, the MicrOmega team at IAS managed to thoroughly develop, test, and calibrate the MicrOmega instrument, and to deliver it to the curation facility of the Hayabusa2 at ISAS, the Japanese Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, on Friday July 3, 2020, after its performances had been demonstrated as excellent.
Although there are evidences of relationships between the most primitive bodies of the solar system and differentiated planetary bodies with a metallic core, no sample has been found up to now that bears information on the onset of planetary differentiation. Researchers have recently described a volcanic rock produced by extremely limited partial melting of a parent body chemically similar to the most primitive meteorites (carbonaceous chondrites) and crystallized upon ascent toward the surface of the body. This sample proves that some carbonaceous bodies from the outer solar system are partially differentiated and is the missing link in a continuum between comets and iron meteorites from metallic planetary cores.
The SPICE instrument on board ESA's Solar Orbiter mission has successfully obtained its first measurements of the Sun on April 21, 2020. This is a major step for the instrument and for the mission, which was launched on February 10, 2020 and is currently on its way to study the Sun closely.
One and a half year after its launch in October 2018, the BepiColombo spacecraft has performed an Earth flyby on April 10, 2020, so as to reach Venus on its way to an orbital insertion around Mercury end of 2025. BepiColombo is the first European mission using ionic propulsion, which makes it possible to implement major changes in the trajectory with a limited impact on the mass budget.